Hurricane Beryl brought wind and rain to east Texas on Monday morning. Beryl weakened to a tropical storm late on Monday morning. At 11:00 a.m. EDT on Monday the center of Tropical Storm Beryl was located at latitude 29.8°N and longitude 95.7°W which put the center about 20 miles (30 km) west-northwest of Houston, Texas. Beryl was moving toward the north at 13 m.p.h. (20 km/h). The maximum sustained wind speed was 70 m.p.h. (110 km/h) and there were wind gusts to 85 m.p.h. (135 km/h). The minimum surface pressure was 984 mb.
A Tropical Storm Warning was in effect for the portion of the coast from Port O’Connor to Sabine Pass, Texas.
A Storm Surge Warning was in effect for the portion of the coast from Port O’Connor to Sabine Pass, Texas.
The center of Hurricane Beryl made landfall on the coast of Texas at Matagorda early on Monday morning. Beryl was intensifying at the time of landfall. The maximum sustained wind speed in Hurricane Beryl was 80 m.p.h. (130 km/h) at the time of landfall. A circular eye with a diameter of 32 miles (52 km) was present at the center of Beryl’s circulation at the time of landfall.
The strongest winds in Hurricane Beryl were occurring in the eastern half of Beryl’s circulation. At the time of landfall winds to hurricane force extended out 45 miles (75 km) in the eastern side of Beryl. Winds to tropical storm force extended out 115 miles (185 km) from the center of Hurricane Beryl.
The Hurricane Intensity Index (HII) for Hurricane Beryl at the time of landfall was 11.5. The Hurricane Size Index (HSI) was 10.3 and the Hurricane Wind Intensity Size Index (HWISI) was 21.8. Hurricane Beryl was not quite as strong as Hurricane Dolly was when Dolly hit South Texas in 2008. Beryl was a little smaller that Dolly was.
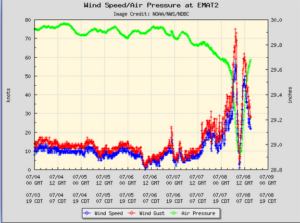
The eye of Hurricane Beryl passed directly over Matagorda, Texas. A weather station at Matagorda, Texas (EMAT2) reported a sustained wind speed of 68 m.p.h. (110 km/h) when the northern part of the eyewall passed over the station. The station also reported a wind gust of 86 m.p.h. (139 km/h). The station reported a surface pressure of 980 mb when the eye of Hurricane Beryl was over it.
A weather station at Freeport, Texas (FPST2) reported a sustained wind speed of 75 m.p.h. (120 km/h) and a wind gust of 87 m.p.h. (141 km/h).
A weather station at the North Jetty Entrance to Galveston Bay (GNJT2) reported a sustained wind speed of 72 m.p.h. (117 km/h) and a wind gust of 82 m.p.h. (132 km/h).
After Hurricane Beryl made landfall on the coast of Texas, the center of Beryl’s circulation passed just to the west of Houston. The eastern side of Beryl’s eyewall passed over Houston. Beryl brought strong winds and heavy rain to the area around Houston.
A weather station at Houston Hobby Airport reported a sustained wind speed of 58 m.p.h. (94 km/h) and a wind gust of 84 m.p.h. 135 km/h). The weather station also reported 4.15 inches (105 mm) of rain.
A weather station at Houston Intercontinental Airport reported a sustained wind speed of 59 m.p.h. (95 km/h) and a wind gust of 82 m.p.h. (132 km/h). The station also reported 4.31 inches of rain.
The strong winds in Hurricane Beryl caused widespread electricity outages in east Texas. There were reports of 2.5 million customers without electricity.
The strong winds in Hurricane Beryl caused a storm surge along the coast of Texas. There were reports of water level rises of 5 feet (1.5 meters) at multiple locations along the coast.
Tropical Storm Beryl will move under the southeastern part of an upper level trough over the Central U.S. The upper level trough will steer Beryl toward the north-northeast during the next 12 hours. On its anticipated track, Tropical Storm Beryl will move over northeast Texas later today. The upper level trough will steer Beryl toward the northeast on Tuesday. Beryl will move over Arkansas on Tuesday morning.
Tropical Storm Beryl will continue to weaken gradually as it moves farther inland. Beryl will continue to produce strong winds over east Texas during the next few hours. Widespread minor wind damage is likely to occur. There are also likely to be additional electricity outages. Tropical Storm Beryl could drop up to 8 inches (200 mm) of rain on some locations. Heavy rain is likely to cause flooding. Flood Watches are in effect for parts of eastern Texas. Flood Watches are also in effect for parts of southeastern Oklahoma, southwestern Arkansas and northwestern Louisiana. Tropical Storm Beryl will continue to cause a storm surge of up to 5 feet (1.5 meters) along the coast until the wind speeds decrease when Beryl moves farther away.