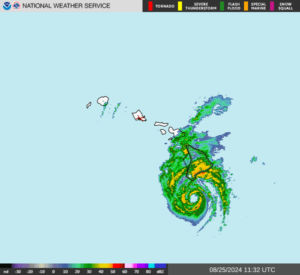
Hurricane Hone brought wind and rain to Hawaii on Sunday. At 11:00 p.m. EDT on Sunday the center of Hurricane Hone was located at latitude 19.1°N and longitude 158.6°W which put the center about 160 miles (260 km) south-southwest of Honolulu, Hawaii. Hone was moving toward the west at 13 m.p.h. (20 km/h). The maximum sustained wind speed was 75 m.p.h. (120 km/h) and there were wind gusts to 90 m.p.h. (145 km/h). The minimum surface pressure was 994 mb.
Bands in the northern side of Hurricane Hone brought wind and rain to the Big Island of Hawaii on Sunday. A weather station at Bradshaw Army Airfield (PHSF) measured a sustained wind speed of 35 m.p.h. (56 km/h) and a wind gust of 44 m.p.h. (71 km/h). The weather station also reported 1.35 inches (34.3 mm) of rain. A weather station at Kahuku reported 8.52 inches (216.4 mm) of rain.
Hurricane Hone weakened on Sunday evening as it passed south of Hawaii. An upper level trough northwest of the Hawaiian Islands was producing southwesterly winds that were blowing toward the top of Hone’s circulation. Those winds were causing strong vertical wind shear and the wind shear was causing Hurricane Hone to weaken. An eye was no longer visible at the center of Hone’s circulation. The wind shear was also causing the distribution of thunderstorms to become asymmetrical. Thunderstorms were still occurring in bands in the eastern part of Hurricane Hone. Bands in the western part of Hone’s circulation consisted primarily of showers and low clouds.
Hurricane force winds were still occurring in the northeastern quadrant of Hurricane Hone. Winds to hurricane force extended out 15 miles (25 km) in the northeastern quadrant of Hone’s circulation. Winds to tropical storm force extended out 90 miles (145 km) from the center of Hurricane Hone.
Hurricane Hone will move through an environment that will be unfavorable for intensification during the next 24 hours. Hone will move over water where the Sea Surface Temperatures are near 27°C. However, the upper level trough northwest of the Hawaiian Islands will continue to cause strong vertical wind shear. The wind shear will cause Hurricane Hone to weaken on Monday.
Hurricane Hone will move around the southern side of a subtropical high pressure system over the Eastern North Pacific and Central Pacific. The high pressure system will steer Hone toward the west-northwest during the next 24 hours. On its anticipated track, Hurricane Hone will move farther away from Hawaii on Monday.
Elsewhere, Hurricane Gilma started to weaken and Tropical Storm Hector formed over the Eastern North Pacific Ocean.
At 11:00 p.m. EDT on Sunday the center of Hurricane Gilma was located at latitude 18.1°N and longitude 135.1°W which put the center about 1310 miles (2110 km) east of Hilo, Hawaii. Gilma was moving toward the west at 9 m.p.h. (15 km/h). The maximum sustained wind speed was 105 m.p.h. (165 km/h) and there were wind gusts to 125 m.p.h. (200 km/h). The minimum surface pressure was 972 mb.
At 11:00 p.m. EDT on Monday the center of Tropical Storm Hector was located at latitude 16.2°N and longitude 123.2°W which put the center about 980 miles (1580 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California. Hector was moving toward the west at 12 m.p.h. (19 km/h). The maximum sustained wind speed was 45 m.p.h. (75 km/h) and there were wind gusts to 60 m.p.h. (95 km/h). The minimum surface pressure was 1001 mb.