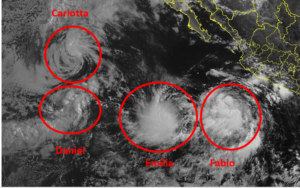
Tropical Storm Fabio formed over the Eastern North Pacific Ocean southwest of Mexico on Monday morning. At 11:00 a.m. EDT on Monday the center of Tropical Storm Fabio was located at latitude 14.8°N and longitude 106.9°W which put the center about 335 miles (540 km) southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico. Fabio was moving toward the northwest at 12 m.p.h. (19 km/h). The maximum sustained wind speed was 40 m.p.h. (65 km/h) and there were wind gusts to 50 m.p.h. (80 km/h). The minimum surface pressure was 1006 mb.
A low pressure system over the Eastern North Pacific Ocean southwest of Mexico strengthened on Monday morning and the U.S. National Hurricane Center designated the system as Tropical Storm Fabio. More thunderstorms formed near the center of Fabio’s circulation. However, the distribution of thunderstorms around Tropical Storm Fabio was asymmetrical. Thunderstorms were occurring in bands in the southern and western parts of Fabio’s circulation. Bands in the northern and eastern parts of Tropical Storm Fabio consisted primarily of showers and lower clouds. Storms near the center of Fabio generated upper level divergence that pumped mass away to the west of the tropical storm.
Winds to tropical storm force extended out 70 miles in the southeastern quadrant of Tropical Storm Fabio. The winds in the other parts of Fabio’s circulation were blowing at less than tropical storm force.
Tropical Storm Fabio will move through an environment somewhat favorable for intensification during the next 24 hours. Fabio will move over water where the Sea Surface Temperatures are near 28°C. It will move under the southern part of an upper level ridge over the Eastern North Pacific Ocean. The ridge will produce easterly winds that will blow toward the top of Fabio’s circulation. Those winds will cause some vertical wind shear, but the shear may not be enough to prevent intensification. The circulation around Fabio could interact with the circulation around Tropical Storm Emilia. Tropical Storm Fabio could intensify during the next 24 hours.
Tropical Storm Fabio is currently being steered by the circulation around Tropical Storm Emilia. Fabio is forecast to be steered toward the northwest during the next 24 hours. On its anticipated track, Tropical Storm Fabio will move farther away from Mexico. There is a chance that the circulations around Fabio and Tropical Storm Emilia could merge into a single circulation.
Elsewhere, Tropical Storms Carlotta, Daniel and Emilia were spinning over the Eastern North Pacific Ocean.
At 11:00 a.m. EDT on Monday the center of Tropical Storm Carlotta was located at latitude 20.4°N and longitude 127.2°W which put the center about 1125 miles (1805 km) west of the southern tip of Baja California. Carlotta was moving toward the west at 9 m.p.h. (15 km/h). The maximum sustained wind speed was 45 m.p.h. (75 km/h) and there were wind gusts to 60 m.p.h. (95 km/h). The minimum surface pressure was 1001 mb.
At 11:00 a.m. EDT on Monday the center of Tropical Storm Daniel was located at latitude 15.6°N and longitude 127.7°W which put the center about 1265 miles (2035 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California. Daniel was moving toward the northeast at 14 m.p.h. (22 km/h). The maximum sustained wind speed was 40 m.p.h. (65 km/h) and there were wind gusts to 50 m.p.h. (80 km/h). The minimum surface pressure was 1005 mb.
At 11:00 a.m. EDT on Monday the center of Tropical Storm Emilia was located at latitude 14.5°N and longitude 114.1°W which put the center about 640 miles (1035 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California. Emilia was moving toward the south-southwest at 5 m.p.h. (8 km/h). The maximum sustained wind speed was 45 m.p.h. (75 km/h) and there were wind gusts to 60 m.p.h. (120 km/h). The minimum surface pressure was 1001 mb.